Taking the 42CrMoA steel 6-cylinder engine crankshaft as an example, the simplified diagram of the crankshaft parts is shown in the figure below. The performance requirements of the crankshaft are: Rm≥840MPa, Rp0.2≥660MPa, A5≥13%, Z≥40%, aK≥78J/cm2. There are 6 connecting rod journals, 7 main journals and 1 oil seal flange. A total of 14 parts need to be hardened, with a hardness of 57~62HRC.
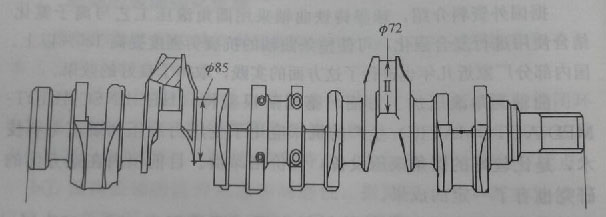
The process of heat treatment of steel crankshaft by medium frequency induction heating power supply is: material inspection → blanking → hot die forging → normalizing → quenching and tempering → cleaning and shot blasting → rough machining → journal surface strengthening treatment → finishing → fluorescent magnetic powder Flaw detection→finished product.
(1) Normalizing the crankshaft: All quenched and tempered crankshafts are made by die forging, and the blanks need to be normalized. The purpose of normalizing is to refine the grain of the forging and prepare the structure for the quenching and tempering treatment.
Crankshaft normalizing is generally carried out using a medium-frequency induction heating power supply. The heating temperature is 840℃±10℃. It is naturally air-cooled after 2.5 hours of heat preservation.
(2) Quenching and tempering of the crankshaft: The quenching and tempering of the crankshaft is carried out on a quenching and tempering unit composed of an intermediate frequency heating power supply and a continuous heating furnace. Currently, there are two better furnace combinations. The first is a connecting rod push furnace, with the crankshaft placed transversely on the material tray, and one tray is pushed into the furnace at regular intervals (one tray is pushed out of the furnace for quenching at the same time). The furnace is wide and low; a continuous chain plate furnace is used for tempering, and the crankshaft is placed on the chain. board conveyor belt. The temperature control of the heating furnace is generally divided into three zones. This combination of equipment has high heat treatment output, good quality, high thermal efficiency of the furnace, and low one-time investment in equipment and low equipment operation and maintenance costs. The second is the continuous hanging furnace, the crankshaft is vertically suspended on the special spreader, and the crankshaft is conveyed by the suspension chain step-by-step into the furnace for heating, and a spreader is moved closer to the furnace at regular intervals (at the same time, a spreader is removed from the furnace for quenching), and in the same way Entering the tempering furnace, compared with the former, the thermal efficiency of the furnace is low, and the one-time investment and operation and maintenance costs of the equipment are high. After quenching and tempering, the crankshaft must be tested for 99% hardness and straightened. After straightening, it needs to be destressed at the tempering temperature, and then shot blasted.
(3) Surface strengthening treatment of the journal: The surface strengthening treatment of the journal is mainly to strengthen the journal and fillets. The surface strengthening methods include induction quenching and nitrocarburizing.
A. Induction hardening is still the preferred strengthening technology for crankshafts (especially crankshafts of high-power engines or supercharged engines).
B. The gas nitrocarburizing treatment of the crankshaft made of 42CrMoA steel is generally carried out by medium frequency induction heating power supply, and the process curve is shown in the figure below:





 en
en  cn
cn  jp
jp  ko
ko  de
de  es
es  it
it  ru
ru  pt
pt  vi
vi  th
th  pl
pl 








 GS-ZP-1200
GS-ZP-1200


