Induction heating for the automotive industry
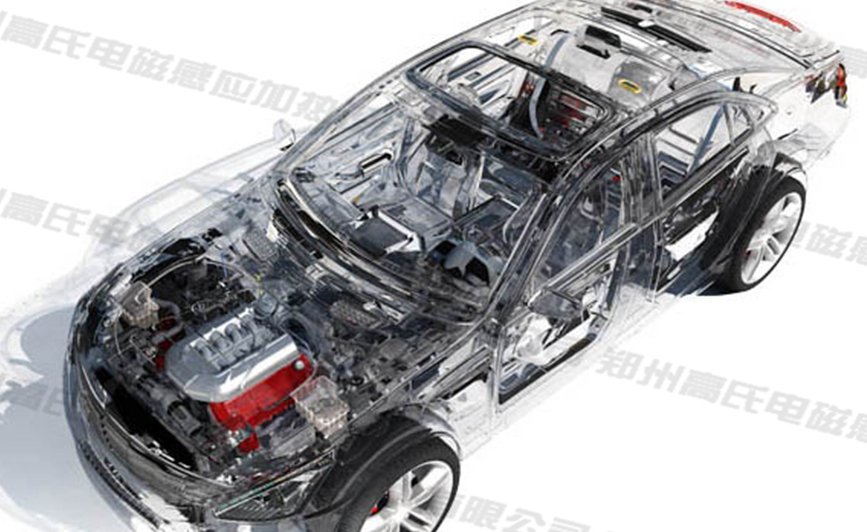
Induction hardening: engine parts such as valves, crankshafts, camshafts, connecting rods and starter rings, transmission components such as CV joints, half shafts, suspension components such as shock absorber rods, springs and suspension arms, automatic and manual gears transmission parts such as ring gears, shift shafts and sun gears, clutch springs and brake pads.
Induction tempering: camshafts, crankshafts, drive shafts, torsion bars, couplings, rocker arms, rock drills, chains, suspension arms, clutches, brake discs, steering wheels, CV joints, shock absorbers, inner and outer races, control rods, valve and output shaft.
Induction preheating: shrink-fitting of transmission components such as gears.
Induction brazing: aluminum components of air-conditioning systems, such as evaporator and condenser connections (tube-to-tube, tube-to-block, tube-to-can) Steel and copper components, such as brake linings, fuel injection pipes motor shorting rings.
Induction bonding: magnets in electric motors, doors, hood and trunk, fenders and mirrors.
Induction straightening: steel chassis, truck manufacture and repair.
After induction heating: engine components and brake discs (polymerization).




 en
en  cn
cn  jp
jp  ko
ko  de
de  es
es  it
it  ru
ru  pt
pt  vi
vi  th
th  pl
pl