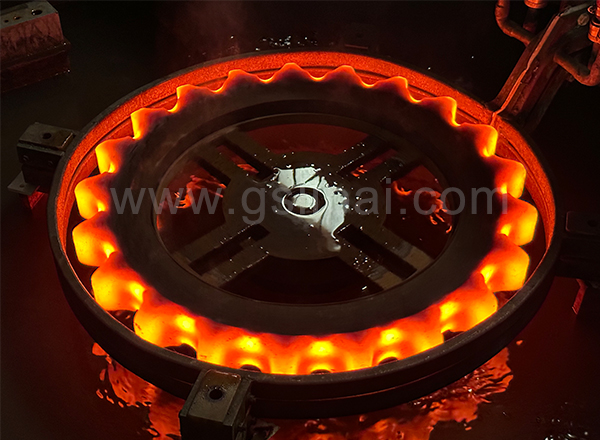
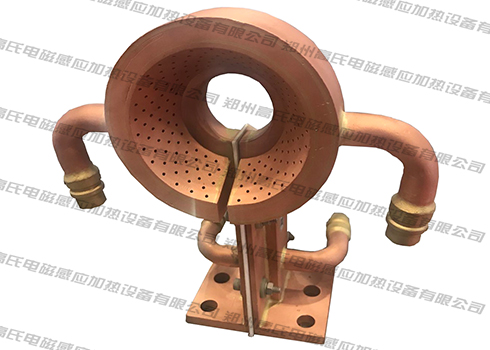
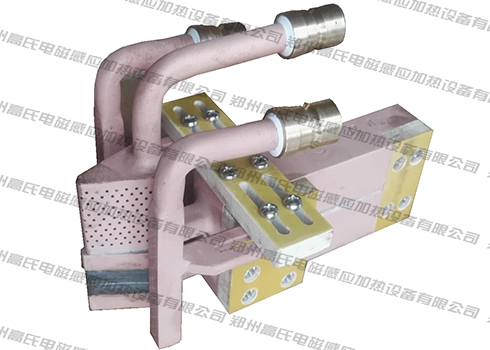
The shaftless rotor of the motor is made of silicon steel sheets, poured into a whole body with aluminum liquid. After being heated to a certain temperature, it is thermally sleeved on the processed shaft. After cooling, the shaftless rotor and the shaft are fixed together to form a rod. Cage rotor. In the past, most manufacturing plants used flame furnaces or resistance furnaces to heat shaftless rotors. In order to improve heating quality and productivity, reduce power consumption and production costs, high-frequency induction heating machines were used to heat shaftless rotors, and relatively good results were achieved. Good results, now used in production.
The outer diameter of the shaftless rotor of the small motor is φ60mm, the inner diameter is φ19mm, the interference is 0.01-0.05mm, the length is 69-89mm, and the mass is 0.7-0.85kg. The heating cycle time is required to be 22 seconds, the heating temperature is 350°C, and the outer surface of the rotor is not allowed to have friction damage. Based on these requirements, it was determined to use a single-piece, vertical, periodic heating method, that is, heating a shaftless rotor to 350°C every 22 seconds to ensure that there is no friction damage on the outer surface of the rotor. The induction coil is spiral-shaped, with an inner diameter of φ95mm and a length of 130mm. It is wound with a square pure copper tube of 10mmx10mmx2mm, and the coil is lined with a tempered glass tube. The high-frequency induction heating machine is 50kw, 10-40khz, and is connected to the induction coil through a high-frequency step-down transformer. The actual test results are that the power is 22kw, the heating time is 22s, and the shaftless rotor reaches 350℃.
A high-frequency induction heating machine is used to heat and heat treat the shaftless rotor of the motor. The produced shaftless rotor of the motor is of good quality and meets the needs of the work. What's even better is that this equipment can greatly improve workers' production efficiency and enable workers to achieve mechanized production.




 en
en  cn
cn  jp
jp  ko
ko  de
de  es
es  it
it  ru
ru  pt
pt  vi
vi  th
th  pl
pl