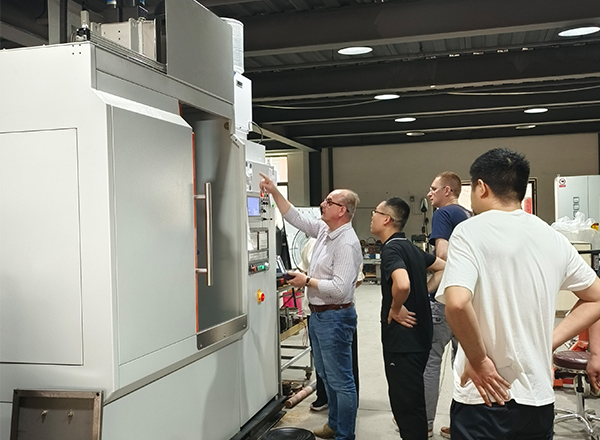
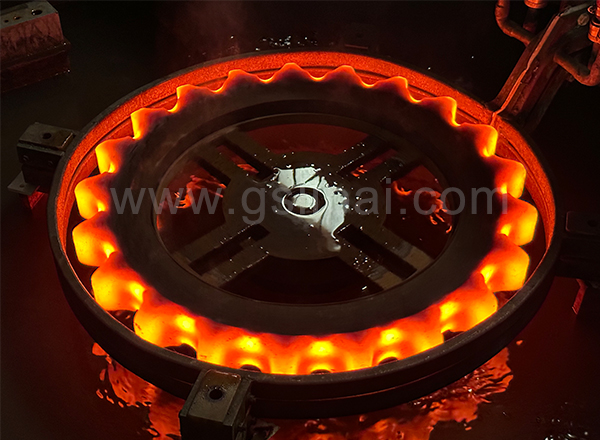
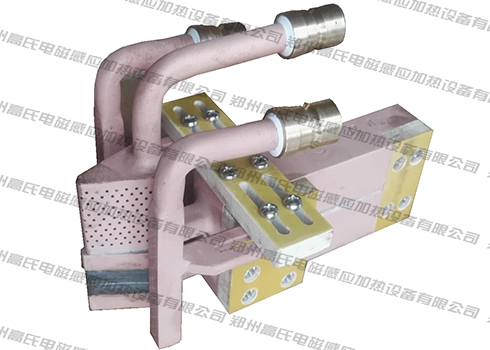
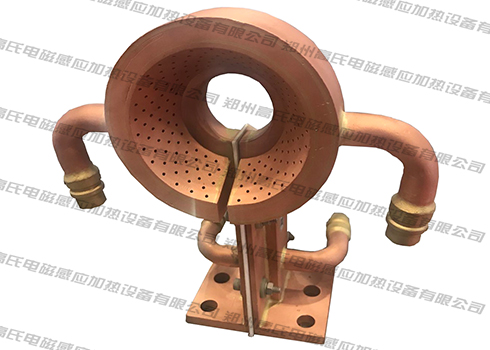
The spline shaft is one of the main shaft parts of the machine tool. In the transmission machinery, it is mainly used to transmit mechanical torque. Working for a long time will cause the spline shaft to be worn or broken, or even scrapped. Therefore, according to its performance, the spline shaft needs to have high strength, good wear resistance and toughness. We usually use national standard structural steel as the material for making the spline shaft, and the heat treatment process uses high-frequency induction heating equipment for quenching.
The mechanical production process of the machine tool spline shaft includes blank forging, quenching and tempering treatment, stress relief annealing treatment, finishing, high frequency induction hardening treatment, tempering treatment, inspection, etc. After the billet is forged, the equipment is heated to quenching and tempering temperature, and the spline shaft is quenched and tempered, mainly to improve the strength, hardness and toughness of the entire shaft part. After quenching and tempering, stress relief annealing is carried out at a temperature of about 580°C. This step is mainly to eliminate the residual stress caused by straightening and avoid or reduce the degree of deformation of the spline shaft. After annealing, we need to perform stress relief annealing on the spline shaft again, mainly to stabilize the dimensional accuracy of the spline shaft, reduce or eliminate the residual stress caused by shaft processing, and prevent the spline shaft from bending deformation before quenching. When the high-frequency induction heating equipment quenches the spline part, due to the shape of the spline teeth, the workpiece must rotate slowly when moving, so as to ensure that the spline teeth can be heated evenly around the spline teeth, and its hardness can be improved. and abrasion resistance. The last two tempering treatments are to eliminate the quenching stress and keep the size and shape of the spline shaft stable.




 en
en  cn
cn  jp
jp  ko
ko  de
de  es
es  it
it  ru
ru  pt
pt  vi
vi  th
th  pl
pl