The lead screw is the key transmission part on various machine tools. It is a transmission and positioning functional component that converts rotary motion into linear motion or converts linear motion into rotary motion. Work is often subjected to bending, torsion, fatigue, impact, and at the same time, it is subject to friction in sliding and rotating parts. The main form of damage to the lead screw is wear and fatigue, so its performance requirements must have good comprehensive mechanical properties (that is, a certain combination of strength and toughness) and high dimensional stability. The relevant working parts (raceways, shaft diameters) High hardness, high strength and sufficient wear resistance are required.
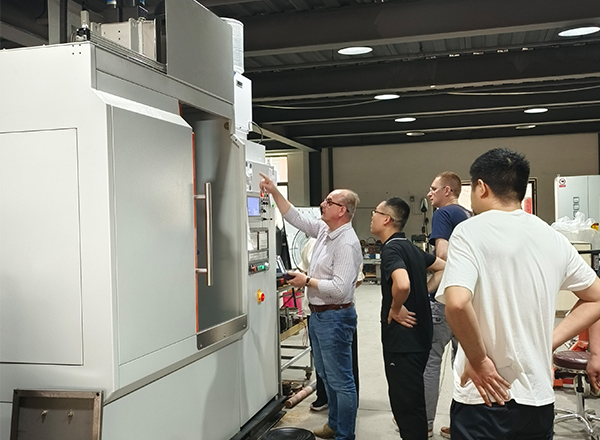
In order to meet the above requirements, the lead screw needs to go through a series of complicated processes, such as material preparation-spheroidizing annealing-machining (rough turning)-quenching and tempering treatment-stress relief annealing-working surface surface quenching, tempering-machining (rough grinding )-aging stress relief treatment-machining (fine grinding), etc. For the quenching process, more and more manufacturers now use all-solid-state high-frequency induction hardening equipment, and the effect is good.
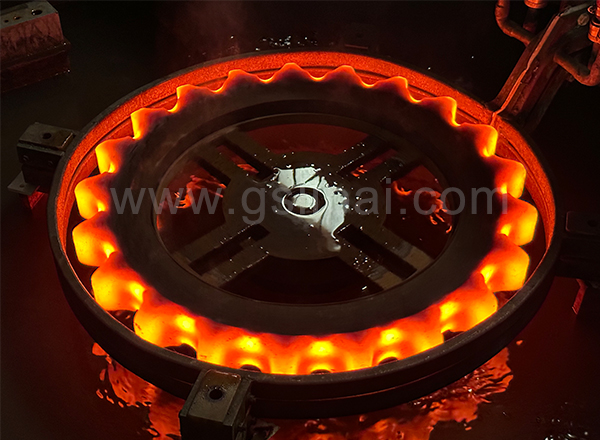
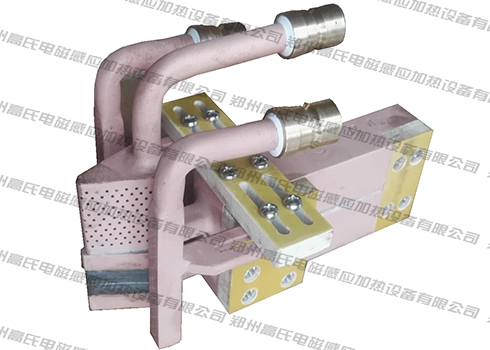
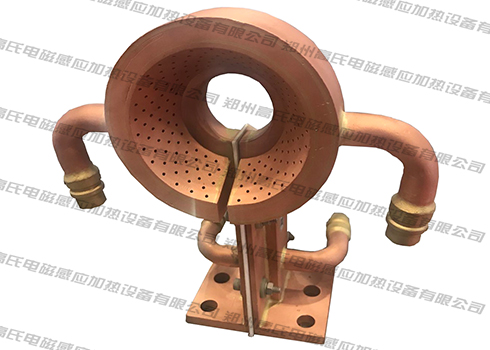
Use all-solid-state high-frequency induction hardening equipment to quench the lead screw. First, make a suitable profiling inductor, then put the part to be quenched into the inductor and heat it to 800-900°C, and then quickly cool it with water. . After quenching by this equipment, the hardness and wear resistance of the lead screw are greatly increased, which meets the requirements of the work, and its wear resistance is further improved.
The all-solid-state high-frequency induction hardening equipment has the function of heating-insulation-cooling three-stage time setting, which is conducive to improving the heating quality and heating cycle, and simplifying manual operation. Even better, the equipment can be used in conjunction with a thermometer to ensure the accuracy of the heating temperature and improve the quenching quality of the workpiece.




 en
en  cn
cn  jp
jp  ko
ko  de
de  es
es  it
it  ru
ru  pt
pt  vi
vi  th
th  pl
pl