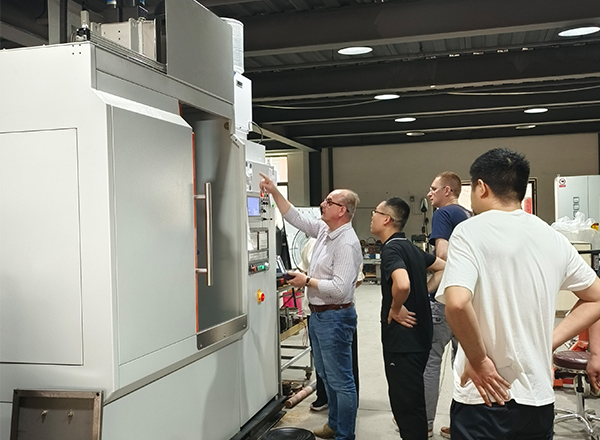
Steering link ball pins, or upper and lower arm control ball studs, are one of the most important parts on a car. Their traditional material is 20CrMnTi, and the traditional heat treatment process is carburizing and quenching. In order to ensure the local hardening of the ball to make it have high wear resistance, to ensure that the neck has good plasticity and toughness, to increase the safety of the ball pin, infiltration Carbon quenching has good processability, requires eight processes successively, and the production cost is very high. Now, we usually use medium frequency induction heating power supply for quenching heat treatment.
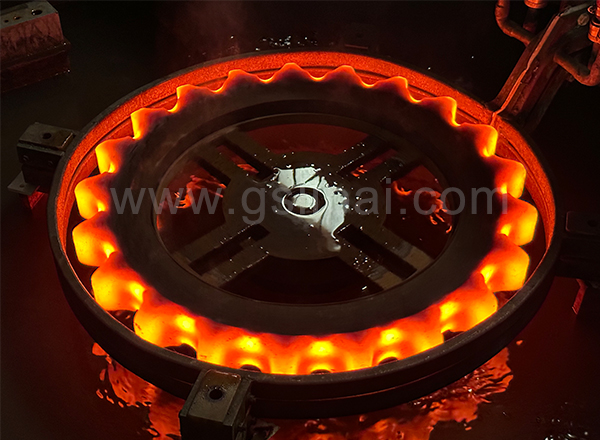
The ball pin is quenched by a medium-frequency induction heating power supply. The feature is that the entire quenching surface of the ball stud is heated by induction at the same time. After reaching the quenching temperature, the sensor sprays water and quenches itself. The parts can be tempered by themselves, and the production efficiency is very high.
Due to the complex shape of the part, the quenching temperature is difficult to be uniform, so the profiling of the hardened layer is not ideal. Therefore, the designer fixed the depth of the hardened layer on the product drawing as 1.5-5.0mm. In fact, the hardened layer is 21 mm in diameter. It is about 1.5mm, and it is very difficult to deepen it. At the largest cross-sectional diameter of the ball head, the hardened layer is about 4.5mm, and it is also difficult to thin it. Even so, the multiple impact life of the intermediate frequency quenched 8KHZ ball stud is still 1.5-3.4 times that of the carburized and quenched ball stud.




 en
en  cn
cn  jp
jp  ko
ko  de
de  es
es  it
it  ru
ru  pt
pt  vi
vi  th
th  pl
pl